1. 자바의 제어문은 크게 두 가지이다.
1) 조건문
2) 반복문
1-1) 조건문 (IF)
public class AccountingAppIF {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double ValueOfSupply = Double.parseDouble(args[0]);
double vatRate = 0.1;
double expenseRate = 0.3;
double vat = ValueOfSupply*vatRate;
double total = ValueOfSupply+vat;
double expense = ValueOfSupply*expenseRate;
double income = ValueOfSupply-expense;
double dividend1;
double dividend2;
double dividend3;
if (income > 10000.0) {
dividend1 = income*0.5;
dividend2 = income*0.3;
dividend3 = income*0.2;
} else {
dividend1 = income*1.0;
dividend2 = income*0;
dividend3 = income*0;
}
System.out.println("Value of supply : " +ValueOfSupply);
System.out.println("VAT : " +vat);
System.out.println("Total : " +total);
System.out.println("Expense : " +expense);
System.out.println("Income : " +income);
System.out.println("Dividend 1: " +dividend1);
System.out.println("Dividend 2: " +dividend2);
System.out.println("Dividend 3: " +dividend3);
}
}
----------------------------------------------------
2. 배열 (Array)
배열 (Array) : 프로젝트의 값과 변수들이 많아지면 혼동되거나 겹칠 수 있으므로 하나의 변수로 나타내기 위하여 배열을 이용한다.
서로 연관된 데이터를 정리정돈 하는 수단이 바로 배열이다.
public class AccountingArrayApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double ValueOfSupply = Double.parseDouble(args[0]);
double vatRate = 0.1;
double expenseRate = 0.3;
double vat = ValueOfSupply*vatRate;
double total = ValueOfSupply+vat;
double expense = ValueOfSupply*expenseRate;
double income = ValueOfSupply-expense;
double[] dividendRates = new double[3];
dividendRates[0]=0.5;
dividendRates[1]=0.3;
dividendRates[2]=0.2;
double dividend1 = income*dividendRates[0];
double dividend2 = income*dividendRates[1];
double dividend3 = income*dividendRates[2];
System.out.println("Value of supply : " +ValueOfSupply);
System.out.println("VAT : " +vat);
System.out.println("Total : " +total);
System.out.println("Expense : " +expense);
System.out.println("Income : " +income);
System.out.println("Dividend 1: " +dividend1);
System.out.println("Dividend 2: " +dividend2);
System.out.println("Dividend 3: " +dividend3);
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------
1-2) 반복문 (Loop)
배열과 반복문은 서로 함께 쓸 때 시너지 효과를 내므로 같이 살펴보는 것이 좋다.
동일한 작업을 여러번 반복할때 반복되는 횟수만큼 코드가 길어지는데 그때 반복문 한 두 줄로 깔끔하게 입력하여 처리할 수 있다.
public class AccountingArrayLoop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double ValueOfSupply = Double.parseDouble(args[0]);
double vatRate = 0.1;
double expenseRate = 0.3;
double vat = ValueOfSupply*vatRate;
double total = ValueOfSupply+vat;
double expense = ValueOfSupply*expenseRate;
double income = ValueOfSupply-expense;
System.out.println("Value of supply : " +ValueOfSupply);
System.out.println("VAT : " +vat);
System.out.println("Total : " +total);
System.out.println("Expense : " +expense);
System.out.println("Income : " +income);
double[] dividendRates = new double[3];
dividendRates[0]=0.5;
dividendRates[1]=0.3;
dividendRates[2]=0.2;
int i = 0;
while(i < dividendRates.length) {
System.out.println("Dividend : " +income*dividendRates[i]);
i = i +1;
}
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
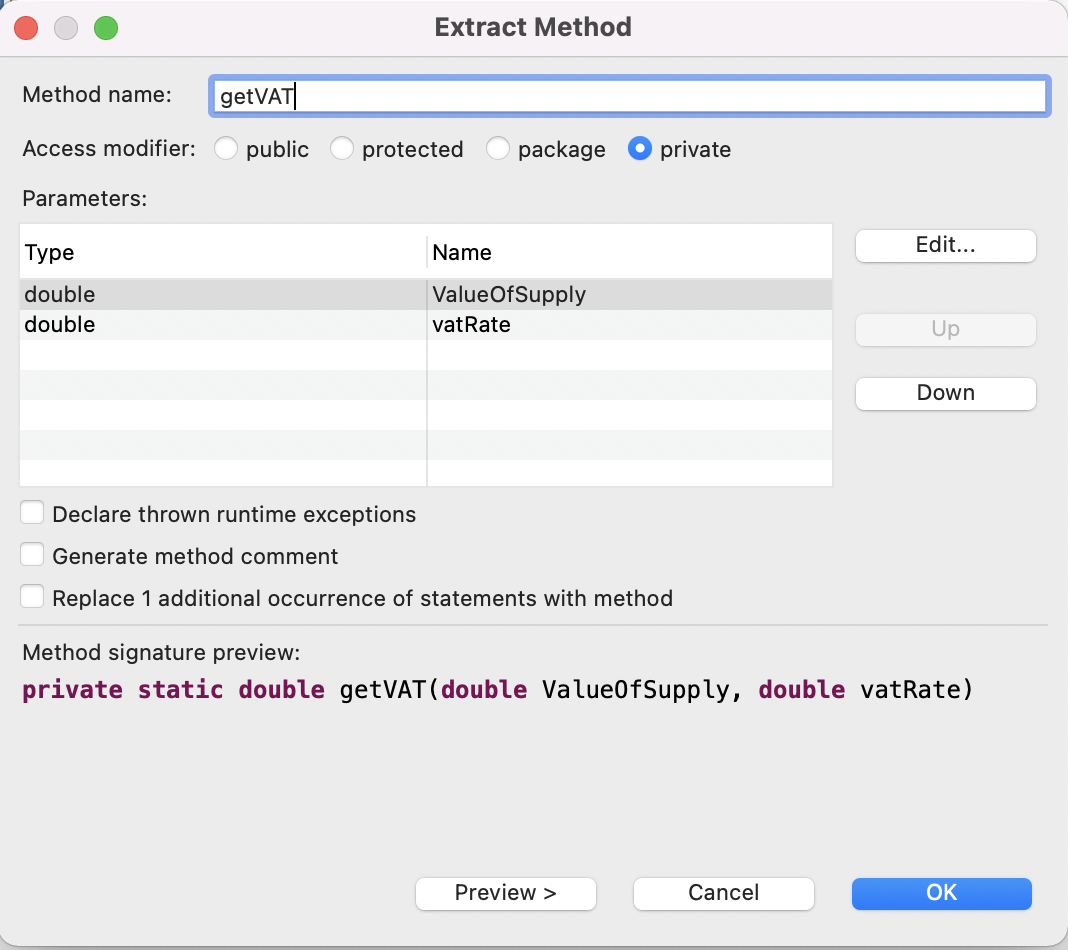
3. 메소드 (method)
메소드(method): 서로 연관된 코드를 그룹핑해서 이름을 붙인 정리 정돈의 상자
public class AccountingMethodApp {
public static double ValueOfSupply;
public static double vatRate;
public static double expenseRate;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ValueOfSupply = 10000.0;
vatRate = 0.1;
expenseRate = 0.3;
print();
}
private static void print() {
System.out.println("Value of supply : " +ValueOfSupply);
System.out.println("VAT : " +getVAT());
System.out.println("Total : " +getTotal());
System.out.println("Expense : " +getExpense());
System.out.println("Income : " +getIncome());
System.out.println("Dividend 1: " +getDividend1());
System.out.println("Dividend 2: " +getDividend2());
System.out.println("Dividend 3: " +getDividend3());
}
public static double getDividend1() {
return getIncome()*0.5;
}
public static double getDividend2() {
return getIncome()*0.3;
}
public static double getDividend3() {
return getIncome()*0.2;
}
public static double getIncome() {
return ValueOfSupply-getExpense();
}
public static double getExpense() {
return ValueOfSupply*expenseRate;
}
public static double getTotal() {
return ValueOfSupply+getVAT();
}
public static double getVAT() {
return ValueOfSupply*vatRate;
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
4. 클래스 (Class)
클래스(Class): 서로 연관된 변수와 메소드를 그룹핑 한 것이다. 그리고 거기에 이름을 붙인 것이다.
class Accounting {
public static double ValueOfSupply;
public static double vatRate;
public static double expenseRate;
static void print() {
System.out.println("Value of supply : " +ValueOfSupply);
System.out.println("VAT : " +getVAT());
System.out.println("Total : " +getTotal());
System.out.println("Expense : " +getExpense());
System.out.println("Income : " +getIncome());
System.out.println("Dividend 1: " +getDividend1());
System.out.println("Dividend 2: " +getDividend2());
System.out.println("Dividend 3: " +getDividend3());
}
public static double getDividend1() {
return getIncome()*0.5;
}
public static double getDividend2() {
return getIncome()*0.3;
}
public static double getDividend3() {
return getIncome()*0.2;
}
public static double getIncome() {
return ValueOfSupply-getExpense();
}
public static double getExpense() {
return ValueOfSupply*expenseRate;
}
public static double getTotal() {
return ValueOfSupply+getVAT();
}
public static double getVAT() {
return ValueOfSupply*vatRate;
}
}
public class AccountingClassApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Accounting.ValueOfSupply = 10000.0;
Accounting.vatRate = 0.1;
Accounting.expenseRate = 0.3;
Accounting.print();
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
5. 인스턴스 (Instance)
인스턴스(Instance) : 하나의 클래스를 복제하여 서로 다른 데이터의 값과 서로 같은 메소드를 가진 복제본을 만드는 것 .
클래스 이름 앞에 new를 붙여서 만든 것. (클래스 내에서 static이 사용되면 안됨)
class Accounting {
public double ValueOfSupply;
public double vatRate;
public double expenseRate;
public void print() {
System.out.println("Value of supply : " +ValueOfSupply);
System.out.println("VAT : " +getVAT());
System.out.println("Total : " +getTotal());
System.out.println("Expense : " +getExpense());
System.out.println("Income : " +getIncome());
System.out.println("Dividend 1: " +getDividend1());
System.out.println("Dividend 2: " +getDividend2());
System.out.println("Dividend 3: " +getDividend3());
}
public double getDividend1() {
return getIncome()*0.5;
}
public double getDividend2() {
return getIncome()*0.3;
}
public double getDividend3() {
return getIncome()*0.2;
}
public double getIncome() {
return ValueOfSupply-getExpense();
}
public double getExpense() {
return ValueOfSupply*expenseRate;
}
public double getTotal() {
return ValueOfSupply+getVAT();
}
public double getVAT() {
return ValueOfSupply*vatRate;
}
}
public class AccountingClassApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//instance
Accounting a1 = new Accounting();
a1.ValueOfSupply = 10000.00;
a1.vatRate = 0.1;
a1.expenseRate = 0.3;
a1.print();
Accounting a2 = new Accounting();
a2.ValueOfSupply = 10000.00;
a2.vatRate = 0.1;
a2.expenseRate = 0.3;
a2.print();
}
}